Audio (but also digital) signals are often transported through wires, because they are often a reliable and easy to make connection. A cable in todays world is at the same time “victim” of the enormous amount of electro-magnetic fields all over. 230V/50Hz net currents that power devices are for audio engineers most noticeable because they cause an audible 50 Hz hum because of induction. When we use unbalanced cables, we can prevent this induction a little by shielding the cable (cage of Faraday), but when these cables are longer than 5m, they still easily pick up hum. Thanks to the differential-amplifier and/or audio transformer, we can get a much bigger noise surpression.
CMRR
Try out almost any circuit with CIRCUITJS
The manual: here
Also look here.
Op Amps are easy to use building blocks for electronic circuits and consist of a number of transistors and fets packed in an IC.
Here some examples of circuits that can be build with Op Amps:
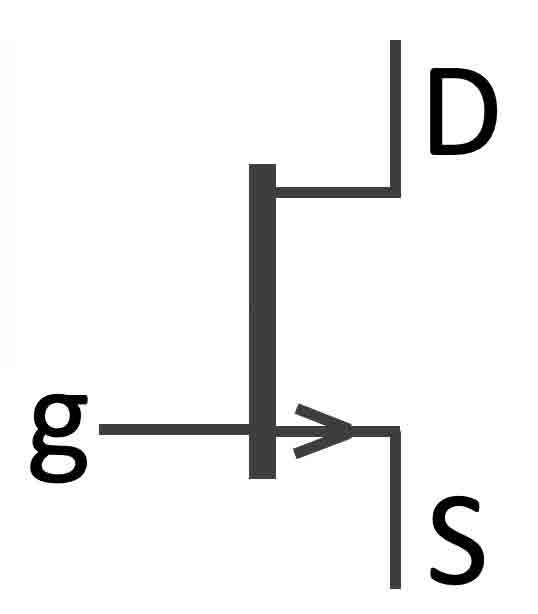
FET stands for Field Effect Transistor. It doesn’t behave like a BJT, it doesn’t amplify a base current. Instead a voltage on the gate (that hardly demands current) opens or closes the current in the source-drain. Hence, the input impedance of a FET can be very high (GOhm). It resembles therefore the behaviour of an electronic tube.
The PDF on FET’s
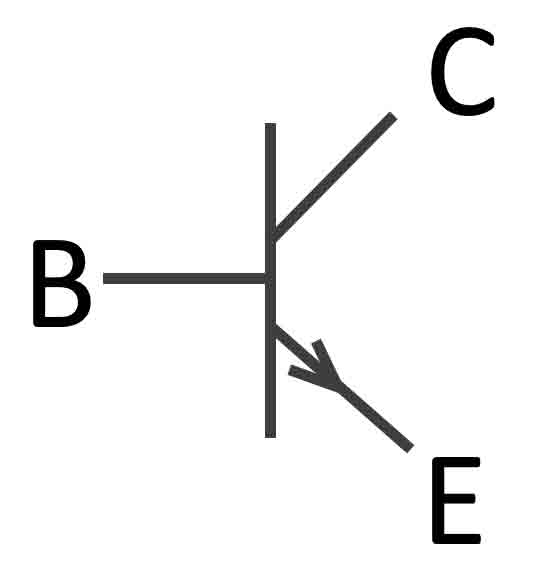
This chapter deals with a very important active component used in electronics. Since the implementation of the BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor), sizes of electronic devices and computers could be shrinked enormously. e.g. In a modern CPU chip a few billion transistors are integrated. Basically a transistor is a (base)current amplifier. It can be used as a switch, a current amplifier , a voltage amplifier and many more things.
A PDF ON TRANSISTORS:
See also here.
There are many ways to make digital Audio connections. Some are point to point (Layer2), some are real network protocol versions (Layer3). Hereunder is a summation of the existing protocols:
Audio Network Types
Basic Electronics for MT1, Network theory and Network audio for MT2, basics of Sounddesign with loudspeakers and the basics of Vectorworks CAD drawing for TTS2. or TTS2. Look in the specific chapters for more information.